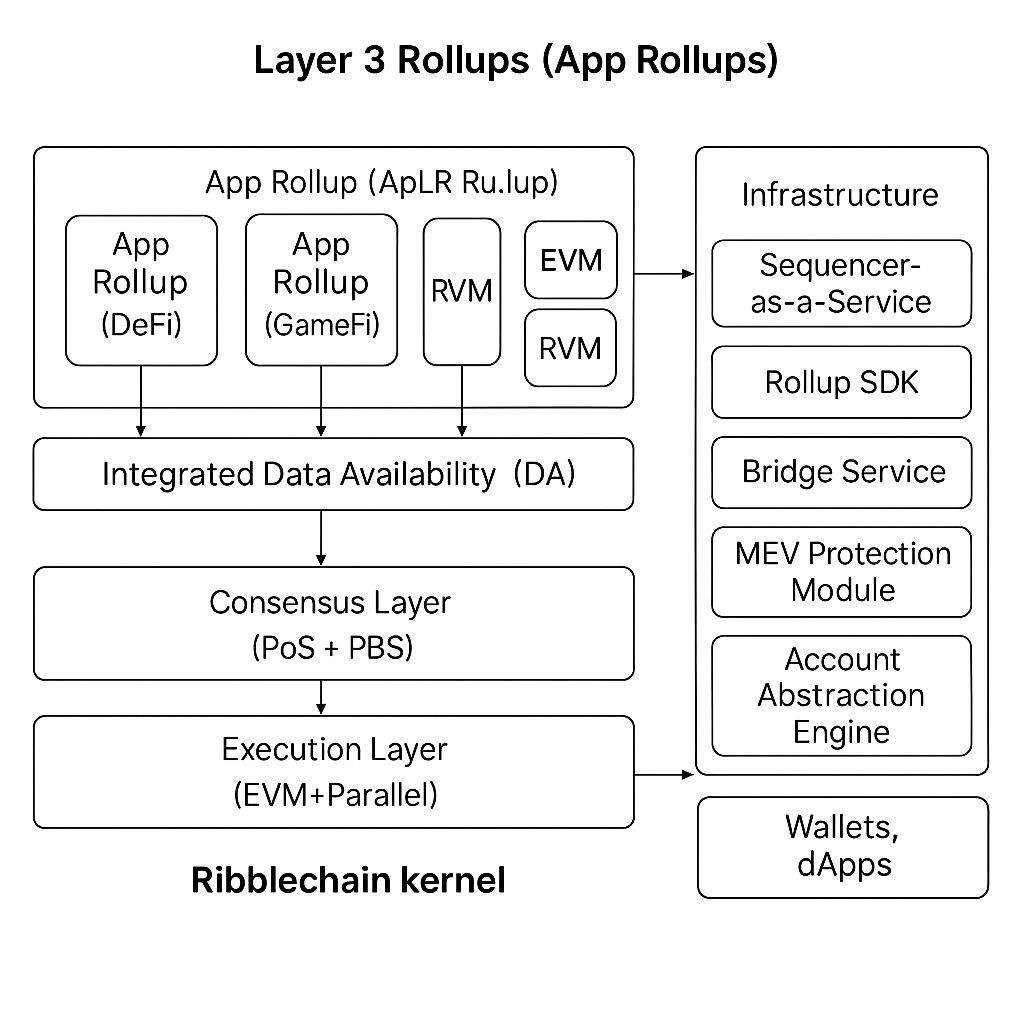
Architecture Overview
RibbleChain is a modular Layer 1 blockchain designed to support Layer 3 (L3) rollups, combining high-performance execution, robust consensus, and scalable data availability. This section outlines RibbleChain's architecture and its core components.
Core Components
-
Execution Layer (EVM++):
- An enhanced Ethereum Virtual Machine with parallel execution for high transaction throughput.
- Supports Solidity smart contracts and batch transactions (inspired by EIP-4844 blobs).
- Compatible with custom VMs (e.g., MoveVM, ZKVM) for L3 rollups.
-
Consensus Layer:
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS) with single-slot finality for rapid transaction confirmation.
- Proposer-Builder Separation (PBS) to mitigate Miner Extractable Value (MEV).
- Inclusion lists and private transactions for fairness and privacy.
-
Data Availability (DA) Layer:
- Integrates with external DA solutions (Celestia, EigenDA) or provides native DA for L3 rollups.
- Ensures cost-efficient and reliable data storage for rollup transactions.
-
Settlement Layer:
- Finalizes transactions from L3 rollups, ensuring security and immutability.
- Provides a unified settlement framework for multi-chain ecosystems.
-
Infrastructure Layer:
- Sequencer-as-a-Service: Enables L3 rollups to deploy custom sequencers.
- Rollup SDK: Tools for developers to build and deploy L3 rollups.
- Native Bridge: Supports cross-chain messaging (LayerZero, IBC).
- Account Abstraction Engine: Native support for ERC-4337 smart wallets.
Layer 3 Rollups
L3 rollups are application-specific chains tailored for use cases like GameFi, DeFi, or SocialFi. Each L3 rollup:
- Runs on a custom sequencer, leveraging RibbleChain's L1 for settlement and DA.
- Supports flexible VM configurations (EVM, ZKVM, MoveVM).
- Integrates with RibbleChain's native bridge for cross-chain interactions.
Diagram
Next Steps
- Start with the Quick Start Guide to engage with RibbleChain.
- Learn about Rollup SDK for building L3 rollups.
- Understand Staking to secure the network.